Abstract
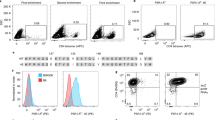
This protocol details a method to identify CD4+ T cells that respond to antigens. The method relies on detection of CD154, a costimulatory cell surface protein that is expressed by CD4+ T cells upon activation, and can be used to purify live CD4+ T cells of diverse function. To detect CD154, fluorescently labeled antibodies are cultured with cell samples, peptides (or whole antigens) and monensin during a 6- to 24-h stimulation period. (Note that the assay is not compatible with brefeldin A.) After stimulation, cells are stained with any other antibodies of interest and then are analyzed by flow cytometry or purified by cell sorting. Unlike other assays, this method allows simultaneous assessment of other cell phenotypes or functions, is compatible with downstream RNA-based assays and preserves cell viability. This protocol can be completed in 9 h.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chattopadhyay, P.K., Yu, J. & Roederer, M. A live-cell assay to detect antigen-specific CD4+ T cells with diverse cytokine profiles. Nat. Med. 11, 1113–1117 (2005).
Brines, R.D. & Klaus, G.G. Polyclonal activation of immature B cells by preactivated T cells: the role of IL-4 and CD40 ligand. Int. Immunol. 5, 1445–1450 (1993).
Kawabe, T. et al. The immune responses in CD40-deficient mice: impaired immunoglobulin class switching and germinal center formation. Immunity 1, 167–178 (1994).
van Kooten, C. & Banchereau, J. CD40-CD40 ligand. J. Leukoc. Biol. 67, 2–17 (2000).
Roy, M., Waldschmidt, T., Aruffo, A., Ledbetter, J.A. & Noelle, R.J. The regulation of the expression of gp39, the CD40 ligand, on normal and cloned CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 151, 2497–2510 (1993).
Yellin, M.J. et al. CD40 molecules induce down-modulation and endocytosis of T cell surface T cell-B cell activating molecule/CD40-L. Potential role in regulating helper effector function. J. Immunol. 152, 598–608 (1994).
Graf, D. et al. A soluble form of TRAP (CD40 ligand) is rapidly released after T cell activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 25, 1749–1754 (1995).
Cohen, G.B., Kaur, A. & Johnson, R.P. Isolation of viable antigen-specific CD4 T cells by CD40L surface trapping. J. Immunol. Methods 302, 103–115 (2005).
Betts, M.R. et al. Sensitive and viable identification of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells by a flow cytometric assay for degranulation. J. Immunol. Methods 281, 65–78 (2003).
Frentsch, M. et al. Direct access to CD4+ T cells specific for defined antigens according to CD154 expression. Nat. Med. 11, 1118–1124 (2005).
Subauste, C.S. et al. Pathogen-specific induction of CD154 is impaired in CD4+ T cells from human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. J. Infect. Dis. 189, 61–70 (2004).
Vanham, G. et al. Decreased CD40 ligand induction in CD4 T cells and dysregulated IL-12 production during HIV infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 117, 335–342 (1999).
Zhang, R., Fichtenbaum, C.J., Hildeman, D.A., Lifson, J.D. & Chougnet, C. CD40 ligand dysregulation in HIV infection: HIV glycoprotein 120 inhibits signaling cascades upstream of CD40 ligand transcription. J. Immunol. 172, 2678–2686 (2004).
Chattopadhyay, P.K., Yu, J. & Roederer, M. De novo expression of CD40L (CD154) identifies antigen-specific CD4+ T-cells that express multiple cytokines. Presented at the 12th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (Boston, Massachusetts, USA, 2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chattopadhyay, P., Yu, J. & Roederer, M. Live-cell assay to detect antigen-specific CD4+ T-cell responses by CD154 expression. Nat Protoc 1, 1–6 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.1
This article is cited by
-
Intravenous Bacille Calmette–Guérin vaccination protects simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques from tuberculosis
Nature Microbiology (2023)
-
LEAFY COTYLEDON1 expression in the endosperm enables embryo maturation in Arabidopsis
Nature Communications (2021)
-
An atypical short-chain dehydrogenase–reductase functions in the relaxation of photoprotective qH in Arabidopsis
Nature Plants (2020)
-
Genome-wide identification of multifunctional laccase gene family in Eucalyptus grandis: potential targets for lignin engineering and stress tolerance
Trees (2020)
-
Models of Autism and Methods for Assessing Autistic-Like Behavior in Animals
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.