Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To study whether an increase of plasma leptin concentrations, as observed in the case of increased body weight, is associated with an inflammatory state.
SUBJECTS: Sixty-three healthy subjects with body mass index (BMI) ranging from 20 to 61 kg/m2.
MEASUREMENTS: Plasma concentrations of leptin, the inflammatory parameter soluble TNF-α receptors (TNFR55 and TNFR75), the acute phase proteins lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP), serum amyloid A (SAA), α-acid glycoprotein (AGP), C-reactive protein (CRP), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and the anti-inflammatory soluble Interleukin-1 decoy receptor (sIL-1RII) were measured.
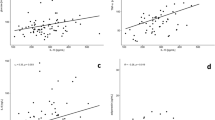
RESULTS: As expected, BMI correlated significantly with leptin (r=0.823, P<0.001), but also with all acute phase proteins, both soluble TNF receptors and PAI concentrations. After correction for BMI and sex, no significant correlation between leptin and the acute phase proteins was seen. Interestingly, however, leptin strongly correlated with both TNF receptors (r=0.523, P<0.001 for TNFR55 and r=0.438, P<0.001 for TNFR75).
CONCLUSIONS: This study shows the development of a pro-inflammatory state with increasing body weight. The BMI independent relationship between leptin and both soluble TNF-receptors is consistent with a regulatory role for leptin in the inflammatory state in morbidly obese subjects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarraf P, Frederich RC, Turner EM, Ma G, Jaskowiak NT, Rivet DJ, Flier JS, Lowell BB, Fraker DL, Alexander HR . Multiple cytokines and acute inflammation raise mouse leptin levels: potential role in inflammatory anorexia J Exp Med 1997 185: 171–175.
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM . Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue Nature 1994 372: 425–432.
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM . Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin resistance J Clin Invest 1995 95: 2409–2415.
Glaum SR, Hara M, Bindokas VP, Lee CC, Polonsky KS, Bell GI, Miller RJ . Leptin, the obese gene product, rapidly modulates synaptic transmission in the hypothalamus Mol Pharmac 1996 50: 230–235.
Halaas JL, Boozer C, Blair West J, Fidahusein N, Denton DA, Friedman JM . Physiological response to long-term peripheral and central leptin infusion in lean and obese mice Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 8878–8883.
Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ, Campfield LA, Burn P, Baskin DG . Identification of targets of leptin action in rat hypothalamus J Clin Invest 1996 98: 1101–1106.
Wang Q, Bing C, Al Barazanji K, Mossakowaska DE, Wang XM, McBay DL, Neville WA, Taddayon M, Pickavance L, Dryden S, Thomas ME, McHale MT, Gloyer IS, Wilson S, Buckingham R, Arch JR, Trayhurn P, Williams G . Interactions between leptin and hypothalamic neuropeptide Y neurons in the control of food intake and energy homeostasis in the rat Diabetes 1997 46: 335–341.
Lee GH, Proenca R, Montez JM, Carroll KM, Darvishzadeh JG, Lee JI, Friedman JM . Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice Nature 1996 379: 632–635.
Mistry AM, Swick AG, Romsos DR . Leptin rapidly lowers food intake and elevates metabolic rates in lean and ob/ob mice J Nutr 1997 127: 2065–2072.
Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Rabinowitz D, Lallone RL, Burley SK, Friedman JM . Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene Science 1995 269: 543–546.
Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB, Hecht R, Winters D, Boone T, Collins F . Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice Science 1995 269: 540–543.
Weigle DS, Bukowski TR, Foster DC, Holderman S, Kramer JM, Lasser G, Lofton DC, Prunkard DE, Raymond C, Kuijper JL . Recombinant ob protein reduces feeding and body weight in the ob/ob mouse J Clin Invest 1995 96: 2065–2070.
Faggioni R, Fuller J, Moser A, Feingold KR, Grunfeld C . LPS-induced anorexia in leptin-deficient (ob/ob) and leptin receptor-deficient (db/db) mice Am J Physiol 1997 273: R181–186.
Faggioni R, Fantuzzi G, Gabay C, Moser A, Dinarello CA, Feingold KR, Grunfeld C . Leptin deficiency enhances sensitivity to endotoxin-induced lethality Am J Physiol 1999 276: R136–R142.
Lord GM, Matarese G, Howard JK, Baker RJ, Bloom SR, Lechler RI . Leptin modulates the T-cell immune response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression Nature 1998 394: 897–901.
Takahashi N, Waelput W, Guisez Y . Leptin is an endogenous protective protein against the toxicity exerted by tumor necrosis factor J Exp Med 1999 189: 207–212.
Kissebah AH, Freedman DS, Peiris AN . Health risks of obesity Med Clin N Am 1989 73: 111–138.
Ross R . Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease New Engl J Med 1999 340: 115–126.
Hazenberg BPC, Limburg PC, Bijzet J, Rijswijk MH . Monoclonal antibody based ELISA for human SAA Amyloid and amyloidosis: Vlth International Symposium on Amyloidosis 1990 p 898.
Hotamisligil GS, Budavari A, Murray D, Spiegelman BM . Reduced tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor in obesity-diabetes. Central role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha J Clin Invest 1994 94: 1543–1549.
Hotamisligil GS, Spiegelman BM . Tumor necrosis factor alpha: a key component of the obesity-diabetes link Diabetes 1994 43: 1271–1278.
Hotamisligil GS, Murray DL, Choy LN, Spiegelman BM . Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits signaling from the insulin receptor Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 4854–4858.
Muller G, Ertl J, Gerl M, Preibisch G . Leptin impairs metabolic actions of insulin in isolated rat adipocytes J Biol Chem 1997 272: 10585–10593.
Cigolini M, Tonoli M, Borgato L, Frigotto L, Manzato F, Zeminian S, Cardinale C, Camin M, Chiaramonte E, De SG, Lunardi C . Expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in human adipose tissue: a role for TNF-alpha? Atherosclerosis 1999 143: 81–90.
Pickup JC, Mattock MB, Chusney GD, Burt D . NIDDM as a disease of the innate immune system: association of acute-phase reactants and interleukin-6 with metabolic syndrome X Diabetologia 1997 40: 1286–1292.
Samad F, Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Pandey M, Hotamisligil GS, Loskutoff DJ . Tumor necrosis factor alpha is a key component in the obesity-linked elevation of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999 96: 6902–6907.
Vgontzas AN, Papanicolaou DA, Bixler EO, Kales A, Tyson K, Chrousos GP . Elevation of plasma cytokines in disorders of excessive daytime sleepiness: role of sleep disturbance and obesity J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 1313–1316.
Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CD, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW . C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction: a potential role for cytokines originating from adipose tissue? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 972–978.
Leeuwenberg JF, Dentener MA, Buurman WA . Lipopolysaccharide LPS-mediated soluble TNF receptor release and TNF receptor expression by monocytes. Role of CD14, LPS binding protein, and bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein J Immunol 1994 152: 5070–5076.
Froon AH, Dentener MA, Greve JW, Ramsay G, Buurman WA . Lipopolysaccharide toxicity-regulating proteins in bacteremia J Infect Dis 1995 171: 1250–1257.
Guven S, El BA, Sonnenberg GE, Wilson CR, Hoffmann RG, Krakower GR, Kissebah AH . Plasma leptin and insulin levels in weight-reduced obese women with normal body mass index: relationships with body composition and insulin Diabetes 1999 48: 347–352.
Van Zee, KJ, Kohno T, Fischer E, Rock CS, Moldawer LL, Lowry SF . Tumor necrosis factor soluble receptors circulate during experimental and clinical inflammation and can protect against excessive tumor necrosis factor alpha in vitro and in vivo Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 4845–4849.
Spinas GA, Keller U, Brockhaus M . Release of soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in relation to circulating TNF during experimental endotoxinemia J Clin Invest 1992 90: 533–536.
Bemelmans MH, Gouma DJ, Buurman WA . LPS induced sTNF-Receptor release in vivo in a murine model: investigation of the role of TNF, IL-1, LIF, IL-1, and IFNY J Immunol 1993 151: 5554–5562.
Aderka D, Engelmann H, Maor Y, Brakebusch C, Wallach D . Stabilization of the bioactivity of tumor necrosis factor by its soluble receptors J Exp Med 1992 175: 323–329.
Bemelmans MH, van Tits LJ, Buurman WA . Tumor necrosis factor: function, release and clearance Crit Rev Immunol 1996 16: 1–11.
Hauner H, Bender M, Haastert B, Hube F . Plasma concentrations of soluble TNF-alpha receptors in obese subjects Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22: 1239–1243.
Corica F, Allegra A, Corsonello A, Buemi M, Calapai G, Ruello A, Nicita MV, Ceruso D . Relationship between plasma leptin levels and the tumor necrosis factor-alpha system in obese subjects Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23: 355–360.
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM . Differential regulation of the p80 tumor necrosis factor receptor in human obesity and insulin resistance Diabetes 1997 46: 451–455.
Loffreda S, Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Karp CL, Brengman ML, Wang DJ, Klein AS, Bulkley GB, Bao C, Noble PW, Lane MD, Diehl AM . Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses FASEB J 1998 12: 57–65.
Schols AM, Creutzberg EC, Buurman WA, Campfield LA, Saris WH, Wouters EF . Plasma leptin is related to proinflammatory status and dietary intake in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999 160: 1220–1226.
Vreugdenhil AC, Dentener MA, Snoek AM, Greve JW, Buurman WA . Lipopolysaccharide binding protein and serum amyloid A secretion by human intestinal epithelial cells during the acute phase response J Immunol 1999 163: 2792–2798.
Martin NB, Jamieson A, Tuffin DP . The effect of interleukin-4 on tumour necrosis factor-alpha induced expression of tissue factor and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells Thromb Haemost 1993 70: 1037–1042.
Salgado A, Boveda JL, Monasterio J, Segura RM, Mourelle M, Gomez JJ, Peracaula R . Inflammatory mediators and their influence on haemostasis Haemostasis 1994 24: 132–138.
Colotta F, Re F, Muzio M, Bertini R, Polentarutti N, Sironi M, Giri JG, Dower SK, Sims JE, Mantovani A . Interleukin-1 type II receptor: a decoy target for IL-1 that is regulated by IL-4 Science 1993 261: 472–475.
Mendall MA, Patel P, Ballam L, Strachan D, Northfield TC . C Reactive protein and its relation to cardiovascular risk factors: a population based cross sectional study Br Med J 1996 312: 1061–1065.
Skolnik EY, Marcusohn J . Inhibition of insulin receptor signaling by TNF: potential role in obesity and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 1996 7: 161–173.
Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Marino MW, Hotamisligil GS . Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking tnf-alpha function Nature 1997 389: 610–614.
Danesh J, Muir J, Wong YK, Ward M, Gallimore JR, Pepys MB . Risk factors for coronary heart disease and acute-phase proteins. A population-based study Eur Heart J 1999 20: 954–959.
Hamsten A, Wiman B, de Faire U, Blomback M . Increased plasma levels of a rapid inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator in young survivors of myocardial infarction New Engl J Med 1985 313: 1557–1563.
Landin K, Tengborn L, Smith U . Elevated fibrinogen and plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) in hypertension are related to metabolic risk factors for cardiovascular disease J Intern Med 1990 227: 273–278.
Lijnen HR, Collen D . Impaired fibrinolysis and the risk for coronary heart disease Circulation 1996 94: 2052–2054.
Clapham JC, Smith SA, Moore GB, Hughes MG, Azam H, Scott A, Jung RT . Plasma leptin concentrations and OB gene expression in subcutaneous-adipose tissue are not regulated acutely by physiological hyperinsulinaemia in lean and obese humans Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1997 21: 179–183.
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL, Caro JF . Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans New Engl J Med 1996 334: 292–295.
Maffei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, Pratley RE, Lee GH, Zhang Y, Fei H, Kim S, Lallone R, Ranganathan S . Leptin levels in human and rodent: measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects Nature Med 1995 1: 1155–1161.
Schwartz MW, Prigeon RL, Kahn SE, Nicolson M, Moore J, Morawiecki A, Boyko EJ, Porte D . Evidence that plasma leptin and insulin levels are associated with body adiposity via different mechanisms Diabetes Care 1997 20: 1476–1481.
Zumbach MS, Boehme MWJ, Wahl P, Stremmel W, Ziegler R, Nawroth PP . Tumor necrosis factor increases serum leptin levels in humans J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 4080–4082.
Orban Z, Remaley AT, Sampson M, Trajanoski Z, Chrousos GP . The differential effect of food intake and beta-adrenergic stimulation on adipose-derived hormones and cytokines in man J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999 84: 2126–2133.
Lin Y, Lee H, Berg AH, Lisanti MP, Shapiro L, Scherer PE . The lipopolysaccharide-activated toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 induces synthesis of the closely related receptor TLR-2 in adipocytes J Biol Chem 2000 275: 24255–24263.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Dr A Mantovani in Milan, and Hycult Biotechnology (Uden, The Netherlands), for providing reagents for the sIL-1 RII Elisa. Furthermore we want to thank Dr T Kooistra, Leiden, The Netherlands for providing the PAI-1 Elisa kit. Supported by AGIKO-stipendium of The Netherlands Organisation of Scientific Research to F.v.D. and by BIO4-CT97-2107 from the European Commission to W.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Dielen, F., van't Veer, C., Schols, A. et al. Increased leptin concentrations correlate with increased concentrations of inflammatory markers in morbidly obese individuals. Int J Obes 25, 1759–1766 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801825
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801825
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effect of C-reactive protein deficiency on insulin resistance reversal in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome through augmented leptin action
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2023)
-
Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Serum Amyloid A Protein: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Obesity Surgery (2023)
-
Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on the metabolic profile and systemic inflammatory status of women with metabolic syndrome: randomized controlled clinical trial
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2023)
-
Recent advances and future avenues in understanding the role of adipose tissue cross talk in mediating skeletal muscle mass and function with ageing
GeroScience (2021)
-
Systemic Inflammation in Severe Obese Patients Undergoing Surgery for Obesity and Weight-Related Diseases
Obesity Surgery (2018)