Abstract
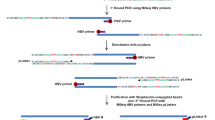
Integration of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA into liver cell DNA has been well established, but its implication in liver carcinogenesis is still being debated. In particular, insertion of the viral genome into cellular genes has been viewed as a rare event. By using HBV-Alu PCR, we have now isolated, from nine hepatocellular carcinomas, nine HBV-DNA integration sites showing that the viral genome mutates key regulatory cellular genes: neurotropic tyrosin receptor kinase 2 (NTRK2) gene, IL-1R-associated kinase 2 (IRAK2) gene, p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (p42MAPK1) gene, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor type 2 (IP3R2) gene, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor (IP3R) type 1 (IP3R1) gene, alpha 2,3 sialyltransferase (ST3GAL VI or SITA) gene, thyroid hormone uncoupling protein (TRUP) gene, EMX2-like gene, and human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) gene. This result brings to 15 the total number of genes targeted by HBV in a study of 22 human liver cancers. Overall, we found that both the inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor gene and the telomerase gene were targeted by HBV in two different tumors. Thus, HBV frequently targets cellular genes involved in cell signalling and some of them may be preferential targets of the viral integration.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berasain C, Patil D, Perara E, Huang SM, Mouly H and Brechot C . (1998). Oncogene, 16, 1277–1288.
Brechot C, Gozuacik D, Murakami Y and Paterlini-Brechot P . (2000). Semin. Cancer Biol., 10, 211–231.
Buendia MA . (1992). Semin. Cancer Biol., 3, 309–320.
Burris TP, Nawaz Z, Tsai MJ and O'Malley BW . (1995). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 9525–9529.
Chami M, Gozuacik D, Saigo K, Capiod T, Falson P, Lecoeur H, Urashima T, Beckmann J, Gougeon ML, Claret M, Maire M, Brechot C and Paterlini-Brechot P . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 2877–2886.
Corcoran L, Adams J, Dunn A and Cory S . (1984). Cell, 37, 113–122.
Dejean A, Bougueleret L, Grzeschik KH and Tiollais P . (1986). Nature, 322, 70–72.
Fourel G, Couturier J, Wei Y, Apiou F, Tiollais P and Buendia M . (1994). EMBO J., 13, 2526–2534.
Fourel G, and Tiollais P . (1994). Primary Liver Cancer: Etiological and Progression Factors. CB. (ed). CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, pp 89–123.
Garcia M, De Thé H, Tiollais P, Samarut J and Dejean A . (1993). Cell Biol., 90, 89–93.
Gozuacik D, Murakami Y, Saigo K, Chami M, Mugnier C, Lagorce D, Okanoue T, Urashima T, Bréchot C and Paterlini-Bréchot P . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 6233–6240.
Graef E, Caselmann WH, Wells J and Koshy R . (1994). Oncogene, 9, 81–87.
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA . (2000). Cell, 100, 57–70.
Horikawa I and Barrett J . (2001). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 93, 1171–1173.
Kroes RA, Jastrow A, McLone MG, Yamamoto H, Colley P, Kersey DS, Yong VW, Mkrdichian E, Cerullo L, Leestma J and Moskal JR . (2000). Cancer Lett., 156, 191–198.
MacDonald T, Brown K, LaFleur B, Peterson K, Lawlor C, Chen Y, Packer R, Cogen P and Stephan D . (2001). Nat. Genet., 29, 143–152.
Matsubara K and Tokino T . (1990). Mol. Biol. Med., 7, 243–260.
Meyerson M . (2000). J. Clin. Oncol., 18, 2626–2634.
Minami M, Poussin K, Brechot C and Paterlini P . (1995). Genomics, 29, 403–408.
Nakashio R, Kitamoto M, Tahara H, Nakanishi T, Ide T and Kajiyama G . (1997). Int. J. Cancer, 74, 141–147.
Nusse R and Varmus H . (1982). Cell, 31, 99–109.
Palsson McDermott E and O'Neill L . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 7808–7815.
Payne G, Bishop J and Varmus H . (1982). Nature, 21, 209–214.
Petretti T, Kemmner W, Schulze B and Schlag PM . (2000). Gut, 46, 359–366.
Pozzan T, Rizzuto R, Volpe P and Meldolesi J . (1994). Physiol. Rev., 74, 595–636.
Robinson WS, Miller RH and Marion PL . (1987). Hepatology, 7, 64S–73S.
Russo G, Ricciardelli G and Pietropaolo C . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 5229–5235.
Scherdin U, Rhodes K and Breindl M . (1990). J. Virol., 64, 907–912.
Schneider F, Kemmner W, Haensch W, Franke G, Gretschel S, Karsten U and Schlag PM . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 4605–4611.
Schröder ARW, Shinn P, Chen H, Berry C, Ecker JR and Bushman F . (2002). Cell, 110, 521–529.
Shibayama E and Koizumi H . (1996). Am. J. Pathol., 148, 1807–1818.
Sugimoto T, Kuroda H, Horii Y, Moritake H, Tanaka T and Hattori S . (2001). Jpn J. Cancer Res., 92, 152–160.
Tahara H, Nakanishi T, Kitamoto M, Nakashio R, Shay J, Tahara E, Kajiyama G and Ide T . (1995). Cancer Res., 55, 2734–2736.
Tu H, Bonura C, Giannini C, Mouly H, Soussan P, Kew M, Paterlini-Bréchot P, Bréchot C and Kremsdorf D . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 7803–7810.
Urashima T, Saigo K, Kobayashi S, Imaseki H, Matsubara H, Koide Y, Asano T, Kondo Y, Koike K and Isono K . (1997). J. Hepatol., 26, 771–778.
Wang J, Chenivesse X, Henglein B and Brechot C . (1990). Nature, 343, 555–557.
Wang Y, Cheong D, Chan S and Hooi SC . (2000). Int. J. Oncol., 16, 757–762.
Weber G, Shen F, Prajda N, Yeh Y, Yang H, Herenyiova M and Look K . (1996). Anticancer Res., 16, 3271–3282.
Yu C, Montoya D, Smith DI and Roberts LR . (2002). 93rd Annual Meeting of American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), Vol. 43. Proceedings. CR. (ed). The American Association for Cancer Research: San Francisco, CA, USA.
Zhu Y, Srivatana U, Ullah A, Gagneja H, Berenson CS and Lance P . (2001). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1536, 148–160.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale), ARC (Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer), FRM (Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale) and LNC (Ligue Nationale contre de Cancer).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paterlini-Bréchot, P., Saigo, K., Murakami, Y. et al. Hepatitis B virus-related insertional mutagenesis occurs frequently in human liver cancers and recurrently targets human telomerase gene. Oncogene 22, 3911–3916 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206492
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206492
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Elevated expression of ISY1, APOA-1, SYNE1, MTG1, and MMP10 at HCC initiation: HCC specific protein network involving interactions of key regulators of lipid metabolism, EGFR signaling, MAPK, and splicing pathways
Protoplasma (2023)
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanism, targeted therapy, and biomarkers
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2023)
-
Major genomic mutations driving hepatocellular carcinoma
Genome Instability & Disease (2023)
-
HBV genome-enriched single cell sequencing revealed heterogeneity in HBV-driven hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
BMC Medical Genomics (2022)
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2021)