Abstract
Background
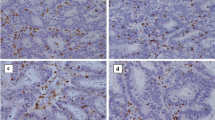
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) counts in colorectal cancer liver metastases (CRCLM) predict survival following resection. While CD4 and CD8 T cells have been correlated with outcome following CRCLM resection, the role of regulatory T cells (Treg) is not well defined.
Methods
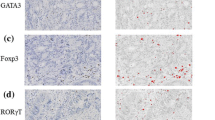
TIL in 188 patients who underwent CRCLM resection between 1998 and 2000 were analyzed by immunohistochemistry using tissue microarrays. Correlation between TIL composition and outcome was determined while controlling for established prognostic factors. Total T cells (CD3), helper T cells (CD4), cytotoxic T cells (CD8), and Treg (FoxP3) were analyzed.
Results
Median follow-up time was 40 months for all patients and 95 months for survivors. Overall survival (OS) at 5 and 10 years was 40 and 25 %, respectively. The CD4 T cell count correlated with OS (p = .02) and recurrence-free survival (p = .04). A high number of CD8 T cells relative to total T cells (CD8:CD3 ratio) predicted longer OS times (p = .05). Analysis of Treg revealed that high FoxP3:CD4 (p = .03) and FoxP3:CD8 (p = .05) ratios were independent predictors of shorter OS. Patients with a high clinical risk score (CRS) were more likely to have a high number of intratumoral Treg, and patients ≥65 years old had a less robust CRCLM T cell infiltration.
Conclusions
A high number of Treg relative to CD4 or CD8 T cells predicted poor outcome, suggesting an immunosuppressive role for FoxP3 + TIL. The intratumoral immune response was an independent predictor of outcome in patients with colorectal liver metastases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clemente CG, Mihm MC, Jr., Bufalino R, Zurrida S, Collini P, Cascinelli N. Prognostic value of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the vertical growth phase of primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer. 1996;77:1303–10.
Fu J, Xu D, Liu Z, Shi M, Zhao P, Fu B, et al. Increased regulatory T cells correlate with CD8 T-cell impairment and poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2328–39.
Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pagès C, et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. 2006;313:1960–4.
Pages F, Berger A, Camus M, Sanchez-Cabo F, Costes A, Molidor R, et al. Effector memory T cells, early metastasis, and survival in colorectal cancer. New Engl J Med. 2005;353:2654–66.
Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D, Gimotty PA, Massobrio M, Regnani G, et al. Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. New Engl J Med. 2003;348:203–13.
Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Berger A, Bindea G, Meatchi T, et al. Histopathologic-based prognostic factors of colorectal cancers are associated with the state of the local immune reaction. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:610–8.
Fong Y, Fortner J, Sun RL, Brennan MF, Blumgart LH. Clinical score for predicting recurrence after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: analysis of 1001 consecutive cases. Ann Surg. 1999;230:309–18 discussion 18–21.
Tomlinson JS, Jarnagin WR, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, Kornprat P, Gonen M, et al. Actual 10-year survival after resection of colorectal liver metastases defines cure. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4575–80.
Katz SC, Pillarisetty VG, Bleier JI, Kingham TP, Chaudhry UI, Shah AB, et al. Conventional liver CD4 T cells are functionally distinct and suppressed by environmental factors. Hepatology. 2005;42:293–300.
Katz SC, Pillarisetty VG, Bleier JI, Shah AB, DeMatteo RP. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells are insufficient to activate T cells. J Immunol. 2004;173:230–5.
Kingham TP, Chaudhry UI, Plitas G, Katz SC, Raab J, DeMatteo RP. Murine liver plasmacytoid dendritic cells become potent immunostimulatory cells after Flt-3 ligand expansion. Hepatology. 2007;45:445–54.
Pillarisetty VG, Shah AB, Miller G, Bleier JI, DeMatteo RP. Liver dendritic cells are less immunogenic than spleen dendritic cells because of differences in subtype composition. J Immunol. 2004;172:1009–17.
Bamboat ZM, Stableford JA, Plitas G, Burt BM, Nguyen HM, Welles AP, et al. Human liver dendritic cells promote T cell hyporesponsiveness. J Immunol. 2009;182:1901–11.
Goubier A, Dubois B, Gheit H, Joubert G, Villard-Truc F, Asselin-Paturel C, et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells mediate oral tolerance. Immunity. 2008;29:464–75.
Katz SC, Pillarisetty V, Bamboat ZM, Shia J, Hedvat C, Gonen M, et al. T cell infiltrate predicts long-term survival following resection of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:2524–30.
Katz SC, Donkor C, Glasgow K, Pillarisetty VG, Gönen M, Espat NJ, et al. T cell infiltrate and outcome following resection of intermediate-grade primary neuroendocrine tumours and liver metastases. HPB (Oxford). 2010;12:674–83.
Cohen T, Prus D, Shia J, Abu-Wasel B, Pinto MG, Freund HR, et al. Expression of P53, P27 and KI-67 in colorectal cancer patients of various ethnic origins: clinical and tissue microarray based analysis. J Surg Oncol. 2008;97:416–22.
Miller R, Siegmund D. Maximally selected chi square statistics. Biometrics. 1982;38:1011–6.
House MG, Ito H, Gonen M, Allen PJ, DeMatteo RP, Brennan MF, et al. Survival after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: trends in outcomes for 1,600 patients during two decades at a single institution. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;210:744–52, 752–5.
Sato E, Olson SH, Ahn J, Bundy B, Nishikawa H, Qian F, et al. Intraepithelial CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and a high CD8 +/regulatory T cell ratio are associated with favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:18538–43.
Halama N, Michel S, Kloor M, Zoernig I, Benner A, Spille A, et al. Localization and density of immune cells in the invasive margin of human colorectal cancer liver metastases are prognostic for response to chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2011;71:5670–7.
Galon J, Fridman WH, Pages F. The adaptive immunologic microenvironment in colorectal cancer: a novel perspective. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1883–6.
Wagner P, Koch M, Nummer D, Palm S, Galindo L, Autenrieth D, et al. Detection and functional analysis of tumor infiltrating T-lymphocytes (TIL) in liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:2310–7. Erratum in: Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:1084. Rahbari, Nuh [added].
Antony PA, Piccirillo CA, Akpinarli A, Finkelstein SE, Speiss PJ, Surman DR, et al. CD8 + T cell immunity against a tumor/self-antigen is augmented by CD4 + T helper cells and hindered by naturally occurring T regulatory cells. J Immunol. 2005;174:2591–601.
Liu WM, Fowler DW, Smith P, Dalgleish AG. Pre-treatment with chemotherapy can enhance the antigenicity and immunogenicity of tumours by promoting adaptive immune responses. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:115–23.
Ma Y, Aymeric L, Locher C, Mattarollo SR, Delahaye NF, Pereira P, et al. Contribution of IL-17-producing gamma delta T cells to the efficacy of anticancer chemotherapy. J Exp Med. 2011;208:491–503.
Melichar B, Touskova M, Vesely P. Effect of irinotecan on the phenotype of peripheral blood leukocyte populations in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002;49:967–70.
Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003;299:1057–61.
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, Hirohashi S. Prevalence of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:5423–34.
Kobayashi N, Hiraoka N, Yamagami W, Ojima H, Kanai Y, Kosuge T, et al. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells affect the development and progression of hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:902–11.
Hirschhorn-Cymerman D, Rizzuto GA, Merghoub T, Cohen AD, Avogadri F, Lesokhin AM, et al. OX40 engagement and chemotherapy combination provides potent antitumor immunity with concomitant regulatory T cell apoptosis. J Exp Med. 2009;206:1103–16.
Quezada SA, Peggs KS, Curran MA, Allison JP. CTLA4 blockade and GM-CSF combination immunotherapy alters the intratumor balance of effector and regulatory T cells. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:1935–45.
Naylor K, Li G, Vallejo AN, Lee WW, Koetz K, Bryl E, et al. The influence of age on T cell generation and TCR diversity. J Immunol. 2005;174:7446–52.
Allan SE, Crome SQ, Crellin NK, Passerini L, Steiner TS, Bacchetta R, et al. Activation-induced FOXP3 in human T effector cells does not suppress proliferation or cytokine production. Int Immunol. 2007;19:345–54.
Morgan ME, van Bilsen JH, Bakker AM, Heemskerk B, Schilham MW, Hartgers FC, et al. Expression of FOXP3 mRNA is not confined to CD4+ CD25+ T regulatory cells in humans. Hum Immunol. 2005;66:13–20.
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ, Topalian SL, Hwu P, et al. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. New Engl J Med. 2012;366:2455–65.
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. New Engl J Med. 2012;366:2443–54.
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. New Engl J Med. 2010;363:711–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katz, S.C., Bamboat, Z.M., Maker, A.V. et al. Regulatory T Cell Infiltration Predicts Outcome Following Resection of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases. Ann Surg Oncol 20, 946–955 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2668-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2668-9