Abstract
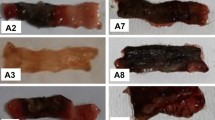
We hypothesized whether systemic administration of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid (HMW HA) could rescue trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis through Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signal. C3H/HeN mice and C3H/HeJ mice were used. Mice were divided into four groups: control, 50% ethanol treatment group, TNBS treatment group, and TNBS plus HA treatment group. The weight changes, clinical scores, macroscopic scores, and histological scores were recorded. Cyclooxygenase 2 (Cox-2) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) expressions were measured both in colons and peritoneal macrophages from these mice. HA was a rescue therapy for the colitis induced by TNBS only in C3H/HeN mice. The clinical score, macroscopic score, and histological score were much lower in C3H/HeN mice receiving TNBS plus HA treatment. Cox-2 and PGE2 expressions only increased in C3H/HeN mice. These Cox-2 expressing cells were macrophages. HA can also promote the production of Cox-2 and PGE2 in peritoneal macrophages from C3H/HeN mice. Our data demonstrated that HMW HA can rescue TNBS-induced colitis through inducing Cox-2 and PGE2 expressions in a TLR4-dependent way. Macrophages may be the effector cells of HMW HA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, K.J., Spicer, A.P., Mascarenhas, M.M., Yu, L., Ochoa, C.D., Garg, H.G., Quinn, D.A., 2005. The role of hyaluronan synthase 3 in ventilator induced lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 172(1):92–98. [doi:10.1164/rccm.200405-652OC]
Boodoo, S., Spannhake, E.W., Powell, J.D., Horton, M.R., 2006. Differential regulation of hyaluronan-induced IL-8 and IP-10 in airway epithelial cells. AJP Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol., 291(3):L479–L486. [doi:10.1152/ajplung.00518.2005]
Breborowicz, A., Połubinska, A., Moberly, J., Ogle, K., Martis, L., Oreopoulos, D., 2001. Hyaluronan modifies inflammatory response and peritoneal permeability during peritonitis in rats. Am. J. Kidney Dis., 37(3):594–600. [doi:10.1016/S0272-6386(01)80018-4]
Collins, C.B., Ho, J., Wilson, T.E., Wermers, J.D., Tlaxca, J.L., Lawrence, M.B., Solga, M., Lannigan, J., Rivera-Nieves, J., 2008. CD44 deficiency attenuates chronic murine ileitis. Gastroenterology, 135(6):1993–2002. [doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.053]
de la Motte, C.A., Hascall, V.C., Calabro, A., Yen-Lieberman, B., Strong, S.A., 1999. Mononuclear leukocytes preferentially bind via CD44 to hyaluronan on human intestinal mucosal smooth muscle cells after virus infection or treatment with poly(I.C). J. Biol. Chem., 274(43): 30747–30755. [doi:10.1074/jbc.274.43.30747]
Deng, J.F., Geng, L., Qian, Y.G., Li, H., Wang, Y., Xie, H.Y., Feng, X.W., Zheng, S.S., 2007. The role of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in acute allograft rejection after liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc., 39(10):3222–3224. [doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2007.02.102]
Földes, G., von Haehling, S., Okonko, D.O., Jankowska, E.A., Poole-Wilson, P.A., Anker, S.D., 2008. Fluvastatin reduces increased blood monocyte Toll-like receptor 4 expression in whole blood from patients with chronic heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol., 124(1):80–85. [doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2006.12.024]
Fukata, M., Chen, A., Klepper, A., Krishnareddy, S., Vamadevan, A.S., Thomas, L.S., Xu, R., Inoue, H., Arditi, M., Dannenberg, A.J., et al., 2006. Cox-2 is regulated by Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) signaling: role in proliferation and apoptosis in the intestine. Gastroenterology, 131(3):862–877. [doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.06.017]
Horton, M.R., McKee, C.M., Bao, C., Liao, F., Farber, J.M., Hodge-DuFour, J., Puré, E., Oliver, B.L., Wright, T.M., Noble, P.W., 1998. Hyaluronan fragments synergize with interferon-γ to induce the C-X-C chemokines Mig and interferon-inducible protein-10 in mouse macrophages. J. Biol. Chem., 273(52):35088–35094. [doi:10.1074/jbc.273.52.35088]
Horton, M.R., Shapiro, S., Bao, C., Lowenstein, C.J., Noble, P.W., 1999. Induction and regulation of macrophage metalloelastase by hyaluronan fragments in mouse macrophages. J. Immunol., 162(7):4171–4176.
Itano, N., Sawani, T., Yoshida, M., Lenas, P., Yamada, Y., Imagawa, M., Shinomura, T., Hamaguchi, M., Yoshida, Y., Ohnuki, Y., et al., 1999. Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have distinct enzymatic properties. J. Biol. Chem., 274(35):25085–25092. [doi:10.1074/jbc.274.35.25085]
Janeway, C.A., Medzhitov, R., 1999. Lipoproteins take their toll on the host. Curr. Biol., 9(23):R879–R882. [doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(00)80073-1]
Jiang, D., Liang, J., Fan, J., Yu, S., Chen, S., Luo, Y., Prestwich, G.D., Mascarenhas, M.M., Garg, H.G., Quinn, D.A., et al., 2005. Regulation of lung injury and repair by Toll-like receptors and hyaluronan. Nat. Med., 11(11): 1173–1179. [doi:10.1038/nm1315]
Lahat, G., Halperin, D., Barazovsky, E.L., Shalit, I., Rabau, M., Klausner, J., Fabian, I., 2007. Immunomodulatory effects of ciprofloxacin in TNBS-induced colitis in mice. Inflamm. Bowel Dis., 13(5):557–565. [doi:10.1002/ibd.20077]
Liu, Y.Y., Lee, C.H., Dedaj, R., Zhao, H., Mrabat, H., Sheidlin, A., Syrkina, O., Huang, P.M., Garg, H.G., Hales, C.A., et al., 2008. High-molecular-weight hyaluronan—a possible new treatment for sepsis-induced lung injury: a preclinical study in mechanically ventilated rats. Crit. Care, 12(4):R102. [doi:10.1186/cc6982]
Majors, A.K., Austin, R.C., de la Motte, C.A., Pyeritz, R.E., Hascall, V.C., Kessler, S.P., Sen, G., Strong, S.A., 2003. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces hyaluronan deposition and leukocyte adhesion. J. Biol. Chem., 278(47): 47223–47231. [doi:10.1074/jbc.M304871200]
Mascarenhas, M.M., Day, R.M., Ochoa, C.D., Choi, W.I., Yu, L., Ouyang, B., Garg, H.G., Hales, C.A., Quinn, D.A., 2004. Low molecular weight hyaluronan from stretched lung enhances IL-8 expression. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 30(1):51–60. [doi:10.1165/rcmb.2002-0167OC]
McKee, C.M., Lowenstein, C.J., Horton, M.R., Wu, J., Bao, C., Chin, B.Y., Choi, A.M., Noble, P.W., 1997. Hyaluronan fragments induce nitric-oxide synthase in murine macrophages through a nuclear factor κB-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem., 272(12):8013–8018. [doi:10.1074/jbc.272.12.8013]
Noble, P.W., McKee, C.M., Cowman, M., Shin, H.S., 1996. Hyaluronan fragments activate an NF-κB/I-κBα autoregulatory loop in murine macrophages. J. Exp. Med., 183(5):2373–2378. [doi:10.1084/jem.183.5.2373]
Połubinska, A., Pawlaczyk, K., Kużlan-Pawlaczyk, M., Wieczorowska-Tobis, K., Chen, C., Moberly, J.B., Martis, L., Breborowicz, A., Oreopoulos, D.G., 2000. Dialysis solution containing hyaluronan: effect on peritoneal permeability and inflammation in rats. Kidney Int., 57(3): 1182–1189. [doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00946.x]
Spicer, A.P., McDonald, J.A., 1998. Characterization and molecular evolution of a vertebrate hyaluronan synthase gene family. J. Biol. Chem., 273(4):1923–1932. [doi:10.1074/jbc.273.4.1923]
Taylor, K.R., Yamasaki, K., Radek, K.A., di Nardo, A., Goodarzi, H., Golenbock, D., Beutler, B., Gallo, R.L., 2007. Recognition of hayluronan released in sterile injury involves a unique receptor complex dependent on Toll-like receptor 4, CD44, and MD-2. J. Biol. Chem., 282(25):18265–18275. [doi:10.1074/jbc.M606352200]
Wallet, M.A., Wallet, S.M., Guiulfo, G., Sleasman, J.W., Goodenow, M.M., 2010. IFN-γ primes macrophages for inflammatory activation by high molecular weight hyaluronan. Cell. Immunol., 262(2):84–88. [doi:10.1016/j. cellimm.2010.02.013]
Wang, C.T., Lin, Y.T., Chiang, B.L., Lin, Y.H., Hou, S.M., 2006. Weight hyaluronic acid down-regulates the gene expression of osteoarthritis-associated cytokines and enzymes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with early osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 14(12):1237–1247. [doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.05.009]
Wang, M.J., Kuo, J.S., Lee, W.W., Huang, H.Y., Chen, W.F., Lin, S.Z., 2006. Translational event mediates differential production of tumor necrosis factor-α in hyaluronanstimulated microglia and macrophages. J. Neurochem., 97(3):857–871. [doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03776.x]
Zhang, X., Shan, P., Qureshi, S., Homer, R., Medzhitov, R., Noble, P.W., Lee, P.J., 2005. Cutting edge: TLR4 deficiency confers susceptibility to lethal oxidant lung injury. J. Immunol., 175(8):4834–4838.
Zhang, Y., Chen, H., Yang, L., 2010. Toll-like receptor 4 participates in gastric mucosal protection through Cox-2 and PGE2. Dig. Liver Dis., 42(7):472–476. [doi:10.1016/j.dld.2009.10.007]
Zheng, L., Riehl, T.E., Stenson, W.F., 2009. Regulation of colonic epithelial repair in mice by Toll-like receptors and hyaluronic acid. Gastroenterology, 137(6):2041–2051. [doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.055]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. C140404) supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Mahaseth, M. & Zhang, Y. Hyaluronic acid as a rescue therapy for trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis through Cox-2 and PGE2 in a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent way. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 12, 712–719 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000362
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000362